DNS servers play critical role in internet communication. Imagine a user try to open google or Microsoft website. But their DNS servers is either down or unreachable. Damn… You are right the solution is having multiple DNS servers for each domain. A server that hold the zone information for a specific website is known as primary or master DNS server. Same way a server having second copy of zone information is called secondary or slave DNS server. Terms primary and secondary DNS can are interchangeable with master and slave DNS.
If you ever registered a domain on the internet, domain registrar will always ask for two name servers to create a TLD (top level domain record). Every though why minimum two are required. Good guess, it is for redundancy. If one goes down, still your public domain information will remain available over the internet. Another benefit is load balancing.

Setup Primary DNS and Create a New Zone
A primary DNS server can be setup using following sequence.
- Open the DNS management console.
- Right click the primary DNS server name and select new zone.
- Click next and select primary zone.
- Click next and select forward or reverse zone.
- Type zone name.
- DNS wizard will ask you to create a new file or use existing file. You can select new file.
- In dynamic updates section, you can select do not allow dynamic updates, continue and click finish. Your primary DNS zone is ready.
Note: In order to allow the zone transfer. You need to add the IP address of secondary DNS server in primary DNS allow zone transfer list. To do so, you need to go to zone properties, zone transfers tab and add the IP of secondary DNS server.
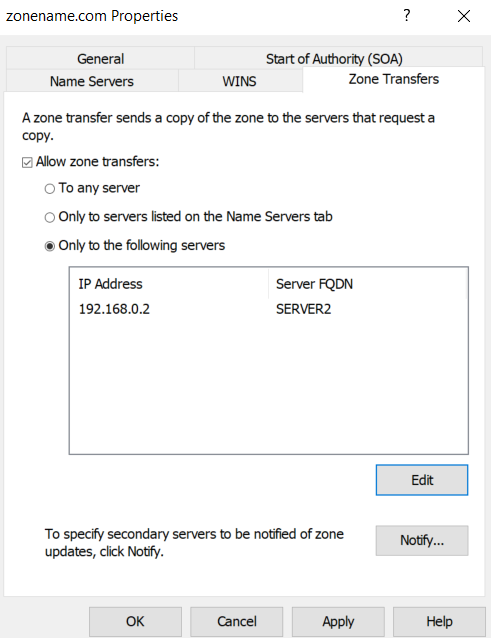
Incase you miss this step you will face zone transfer error while configuring secondary DNS. Lets configure secondary DNS server now.

Setup Secondary DNS and Load Zone from Primary DNS
A secondary DNS server can be setup using following sequence.
- Open the DNS management console.
- Right click the secondary DNS server name and select new zone.
- Click next and select secondary zone.
- Type the zone name and next.
- Enter the IP address of master server.
- You will find a green arrow with show validation status is OK.
- Click next and finish.
Your primary (master) and secondary (slave) DNS servers are ready now.
Primary and Secondary DNS Synchronization
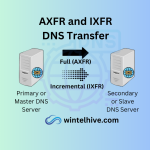
A primary or master DNS zone has a writable zone file for domain. It means if I’ve to create a new record for wintelhive.com. I will create a newrecord.wintelhive.com in primary DNS server. Secondary DNS servers go frequently to the primary server read the zone file update the information accordingly. This process is called zone transfer. DNS zone transfer uses the AXFR/IXFR protocol to sync b/w primary and secondary DNS. It required TCP port 53 communication. Remember the secondary or slave DNS information is no writeable directly by domain/zone owner. It must obtain the information from primary servers to update itself.
Multi Master DNS
As its name reflects, a multimeter DNS has no slave. All DNS servers participating are writable. They can sync each other. This is advanced type of DNS. Microsoft Active directory DNS is a typical example of multi master architecture. In active directory, administrator don’t need to maintain one specific DNS. Microsoft uses active directory sync as a backend process of multi master architecture. They call it active directory integrated zones. Other multi master DNS solution provides either used some sort of database sync in the backend of propriety syncing mechanism to make sure all all participants of DNS infrastructure are capable or writing and updating each other.
DNS Common Misconceptions
- DNS server itself is not primary or secondary. Infect DNS zone is primary or secondary. One DNS can act as primary for one zone and it could act as secondary server for another domain using a different zone file.
- Also some people believe primary DNS is authoritative and secondary is non-authoritative. Its not true. Basically both are authoritative for that domain. So to understand the difference b/w authoritative and non authoritative DNS you can go thorough our article “Authoritative vs Non Authoritative DNS“.
-
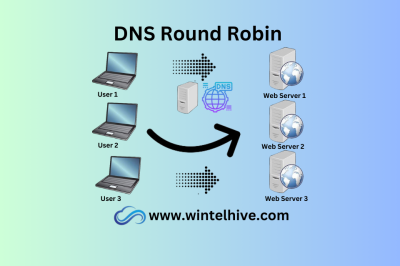
DNS Rebound Robin
Discover how DNS round robin can effortlessly balance traffic across multiple servers, boosting your website’s performance and reliability.
-
What Is DNS Ad Blocking
Learn how DNS ad blocking stops ads at the network level, boosting speed, protecting privacy, and improving browsing in your network.





Leave a Reply